In various industries, from aerospace to automotive, the demand for precision components like Tiny O Rings is on the rise. According to a report by Global Market Insights, the global O-ring market is expected to see significant growth, driven by the increasing use of these critical seals in diverse applications. Tiny O Rings, with their compact size and versatility, play a vital role in ensuring fluid and gas containment, thus contributing to the efficiency and safety of mechanical systems.
Selecting the right Tiny O Rings for your projects is essential, as their performance can greatly influence the integrity and reliability of the entire assembly. The right material, size, and design are critical factors that determine how well these components will function under varying temperatures and pressures. Furthermore, industry standards set forth by organizations such as ASTM International emphasize the importance of choosing the correct specifications to ensure compliance with safety regulations and operational effectiveness. As such, understanding the nuances of Tiny O Rings not only enhances product performance but also helps reduce maintenance costs and increase the lifecycle of the equipment in which they are used.

Tiny O rings are versatile seals used across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Their small, circular shape allows them to create secure seals in tight spaces, effectively preventing leakage of fluids and gases. Understanding the materials used for tiny O rings, such as rubber, silicone, and fluoropolymer compounds, is crucial. Each material has unique physical properties.
For instance, silicone O rings can withstand extreme temperatures, while fluoropolymer options provide excellent chemical resistance. According to a recent market analysis, the global O ring market is expected to reach $1.5 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand in various sectors.
When choosing tiny O rings for your projects, consider compatibility with the fluids they'll encounter. Ensure that the material of the O ring is resistant to chemicals it will be exposed to. Additionally, look into the temperature and pressure ratings of the O rings, as these factors can significantly affect their performance and durability.
Tip: Always measure the groove size accurately before selecting an O ring to guarantee a proper fit. Another important consideration is the durometer, which measures the hardness of the O ring material. A softer O ring can provide a better seal, while a harder one may last longer under tough conditions.
Ultimately, careful selection based on these factors can increase the efficiency and longevity of your seals in practical applications.
When selecting tiny O rings for various applications, the choice of material is crucial as it directly influences the performance and longevity of the product. Common materials for O rings include nitrile rubber, silicone, and fluoropolymers, each offering distinct advantages based on environmental and mechanical requirements. For instance, a report by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) indicates that nitrile rubber is preferred in automotive applications due to its excellent resistance to fuel and oil, while silicone O rings are often selected for high-temperature applications, withstanding temperatures up to 300°F without losing their integrity.
In addition to temperature and chemical resistance, considering factors such as durometer hardness is vital. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the ideal durometer for O rings typically ranges between 70A and 90A for general applications. This hardness level provides the necessary flexibility and compression set resistance. Furthermore, large-scale studies by the Rubber Manufacturers Association highlight that improper material selection can lead to premature failure, costing industries millions in avoidable downtime and repairs. By carefully assessing the specific requirements of your project, including the operating environment and compatibility issues, you can ensure that you choose the right material for your tiny O ring needs, substantially enhancing the reliability of your applications.

When embarking on projects that require tiny O rings, determining the correct size is crucial for achieving optimal performance. According to industry data, a staggering 70% of failures in sealing applications can be attributed to improper sizing. This underscores the importance of accurate measurements—both inside diameter (ID) and cross-sectional thickness—when selecting O rings for specific applications. Using precise measurement tools, such as calipers, can help ensure you choose the right size to create an effective seal, facilitating the longevity and reliability of your project.
One of the essential tips when selecting tiny O rings is to consider the material that's best suited for your application. Different materials can withstand varying temperatures and chemical exposures, which may affect the O ring’s performance. For instance, fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) is ideal for applications requiring high-temperature resistance, while silicone rubber may be preferable in environments that demand flexibility. Additionally, always be aware of the application’s pressure conditions; according to a study published in the Journal of Sealing Technology, improper O ring sizing can lead to leakage as pressure increases.
Ultimately, it is essential to verify the tolerances for both the ID and cross-section against your project requirements. Using O rings with the correct tolerances not only enhances performance but also minimizes the risk of premature failure. Monitoring factors like compression set and resistance to squeeze–two crucial aspects in the longevity of O rings–will ensure your selection meets the demands of the specific application, ensuring functionality and durability throughout its use.
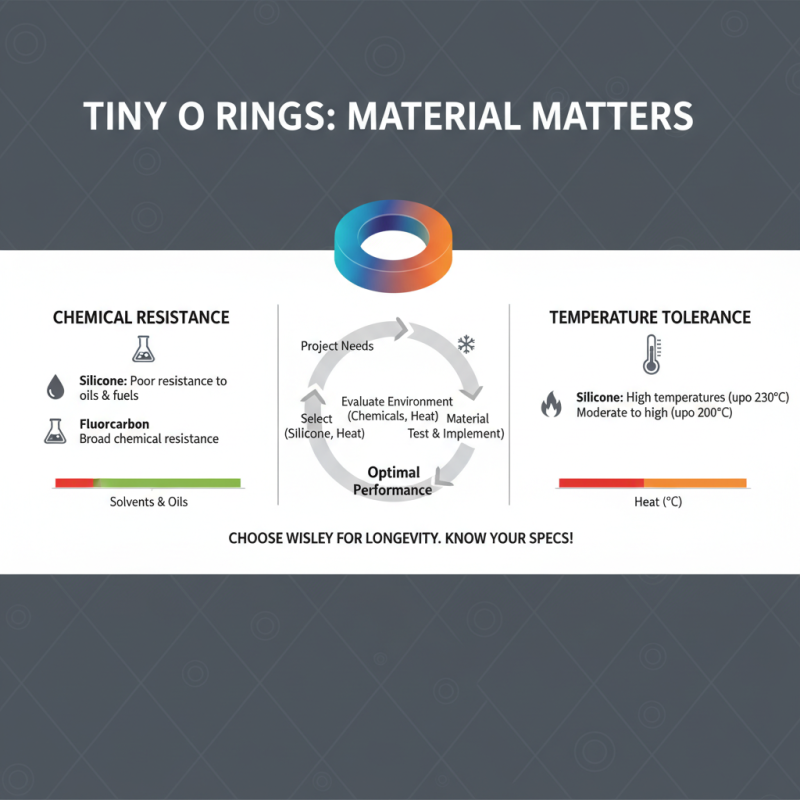
When selecting tiny O rings for your projects, evaluating their chemical resistance and temperature tolerance is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Different materials exhibit varying levels of resistance to solvents, oils, and other substances, which can drastically affect their functionality in diverse environments. For example, silicone O rings may perform well in high-temperature applications but may not withstand certain oils, while fluorocarbon O rings can resist a broader range of chemicals. Therefore, it is essential to understand the specific requirements of your application and choose materials that align with those needs.
In addition to chemical compatibility, temperature tolerance is another vital factor to consider. Each material has a specific temperature range within which it maintains its integrity and performance. As temperatures rise or fall outside these limits, O rings can become brittle or lose their elasticity, leading to potential failures in sealing performance. When assessing your project's requirements, it is advisable to consult resources or technical data sheets that provide information on the thermal stability of different O ring materials. By carefully evaluating both chemical resistance and temperature tolerance, you can select the right tiny O rings that will not only meet but exceed the demands of your application.
When selecting tiny O rings for specific applications, it is crucial to take into account the environmental conditions and chemical exposure they will face. Different materials offer varying levels of resistance to temperature extremes, UV radiation, moisture, and corrosive substances. For instance, if the O rings will be used in a high-temperature environment, materials like silicone or fluorocarbon may be more suitable due to their ability to maintain elasticity and structural integrity under heat. On the other hand, applications involving exposure to oils or chemicals may require materials such as nitrile or Viton, which can withstand such interactions without degrading rapidly.
Additionally, the dimensions and cross-sectional shape of the O rings must align with the design specifics of the project. Ensuring a proper fit is essential not only for the effectiveness of the seal but also for its longevity. A poorly fitted O ring can lead to leaks, which could compromise the functionality of the entire system. Furthermore, understanding the pressure ranges that the O rings will encounter is vital; this will dictate the thickness and diameter required for optimal performance. Therefore, a thorough assessment of project requirements will enable the selection of the right tiny O rings, ultimately ensuring the success and reliability of the application.
| Tip # | Consideration | Material Options | Temperature Resistance | Pressure Ratings | Chemical Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Choose the right size | Nitrile, Silicone | -40°C to 100°C | Up to 300 psi | Good with oil and water |
| 2 | Evaluate the environment | Fluoroelastomer, EPDM | -20°C to 200°C | Up to 500 psi | Excellent for harsh chemicals |
| 3 | Assess the application | Polyurethane, PTFE | -40°C to 120°C | Up to 600 psi | Compatible with various solvents |
| 4 | Consider elasticity | Silicone, Nitrile | -60°C to 200°C | Up to 350 psi | Good with air and water |
| 5 | Inspect for defects | Buna-N, EPDM | -30°C to 100°C | Up to 400 psi | Moderate chemical resistance |
| 6 | Check tolerances | Fluoroelastomer, PTFE | -10°C to 150°C | Up to 300 psi | High resistance to chemicals |
| 7 | Test for compatibility | Silicone, Nitrile | -50°C to 200°C | Up to 450 psi | Good with gaseous applications |
| 8 | Review lifecycle | Polyurethane, EPDM | -20°C to 130°C | Up to 500 psi | Good resistance to abrasion |
| 9 | Plan for installation | Nitrile, Fluoroelastomer | -40°C to 180°C | Up to 400 psi | Moderate to high chemical resistance |
| 10 | Seek expert advice | Various materials available | -60°C to 250°C | Up to 700 psi | Wide chemical compatibility |